Ever wondered how databases magically retrieve data in milliseconds? The secret sauce is B-tree indexes – the unsung heroes of database performance! As a software engineer who’s battled database performance challenges for over a decade, I’m excited to pull back the curtain on these incredible data structures.
The B-Tree: Your Database’s High-Performance Navigator 🗺️
Imagine a massive library where finding a specific book would take hours of searching. B-tree indexes are like a hyper-efficient librarian, instantly pointing you to exactly the right shelf, page, and book. These self-balancing tree structures are the GPS of database technology, guiding queries with remarkable precision.
Why B-Trees Matter in Real-World Applications
From Amazon’s massive e-commerce platform to Google’s search algorithms, B-tree indexes are the backbone of lightning-fast data retrieval. They’re not just a theoretical concept – they’re a practical necessity in modern computing.
The Memory Management Magic 🧙♂️
Here’s the cool part: databases don’t load entire indexes into memory. Why? It’s all about smart resource management.
Memory is Precious (and Expensive!)
- Fact: A full index can be larger than the data it indexes
- Challenge: Limited RAM resources
- Solution: Intelligent page loading
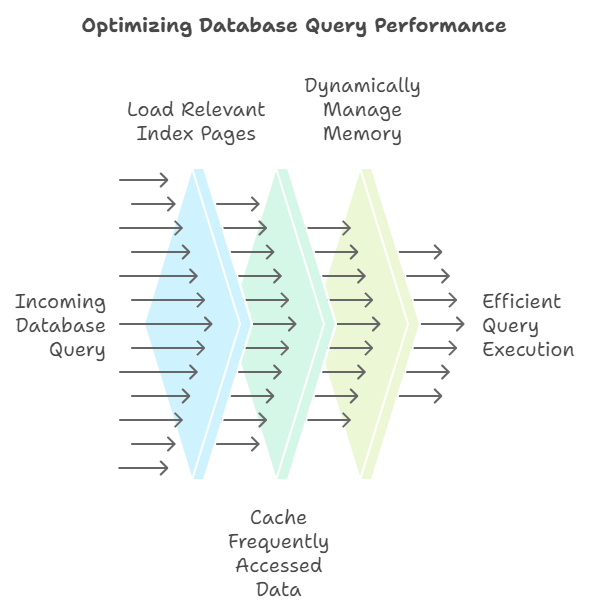
How Databases Play the Memory Game
When a query comes in, the database does something brilliant:
- Loads only the most relevant index pages
- Caches frequently accessed data
- Dynamically manages memory like a chess grandmaster
Real-World Performance in Action 💡
Let’s break down a practical scenario:
sql-- Imagine searching for recent customer orders
SELECT * FROM orders
WHERE order_date BETWEEN '2023-01-01' AND '2023-06-30'
Behind the scenes:
- The B-tree index identifies the exact pages
- Loads only the necessary memory segments
- Retrieves results in milliseconds
The Caching Algorithms: Unsung Heroes
Databases use sophisticated algorithms like:
- Least Recently Used (LRU)
- Clock Algorithm
- Adaptive Replacement Cache (ARC)
These ensure only the most critical index pages stay in memory.
Performance Breakdown 📊
| Memory Strategy | Access Time | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Full Index Load | Slow | Low |
| Selective Loading | Fast | High |
Pro Tips for Developers 🛠️
- Index Wisely: Not all columns need indexing
- Monitor Performance: Use explain analyze
- Right-Size Indexes: Trim unnecessary complexity
Common Misconceptions Debunked 🕵️♂️
- Myth: More indexes always mean faster queries
- Reality: Unnecessary indexes can slow down write operations
FAQ: Your B-Tree Index Questions Answered
📘 What Exactly is a B-Tree Index?
A self-balancing tree structure that keeps data sorted and enables quick searches, insertions, and deletions.
🔍 How Much Memory Do B-Tree Indexes Use?
It varies, but typically 10-30% of total database memory, dynamically allocated.
⚡ Can B-Tree Indexes Work with Any Database?
Yes! MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle – they all use B-tree indexes.
💾 Do B-Tree Indexes Work for All Data Types?
Primarily great for ordered data: integers, timestamps, strings.
The Human Touch 🤝
Database optimization isn’t just about algorithms – it’s about understanding how data moves, breathes, and tells its story.
Learning Resources
Final Thoughts: The Symphony of Data 🎵
B-tree indexes are more than technical constructs – they’re the conductors of our digital information orchestra, ensuring every query plays in perfect harmony.
Pro Tip: Always measure, never guess. Performance is about intelligent design, not just raw power.
About the Author: A software engineer with 12+ years of experience, specializing in database performance and distributed systems. Currently helping teams build scalable, lightning-fast applications.
Next: The Ultimate Guide to Distributed Transactions in 2024



![Distributed Caching Deep Dive: From Basics to Best Practices [Updated] distributed caching](https://devnotes.tech/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/distributed-caching-150x150.jpg)

2 thoughts on “How B-Tree Indexes Power Lightning-Fast Database Queries 🚀”